The Black Sea has a complicated history, during which it several times acquired the status of a salty sea, and then became a freshwater lake. This is due to the antiquity of its origin and the complexity of its geological history.
And originally the Black Sea was part of the ancient Tethys Ocean, once connecting the Pacific to the Atlantic. Later, giant movements of the Earth’s crust took place on the site of the ancient Thetis in the area of modern Asia Minor and the Caucasus.
It has undergone major changes in the course of geological catastrophes for more than one million years. The result was the formation of the mountain systems that still exist today, and the ocean was greatly reduced in size and turned into separate seas.
At the place of the Black Sea, which we know today, various bodies of water have appeared and disappeared. They were either connected to the ocean and became salty, or they lost that connection, became considerably desalinated, and turned into a huge lake.
Accordingly, the ancient animals and fish that lived in salt water changed to those adapted only to fresh water. This has been going on for millions of years. Let us begin to tell the history of the Black Sea from the ancient continents of Gondwana and Eurasia.
The geological past of the Black Sea
In the part of Eurasia, where the Black Sea now spreads, in the distant past, various geological catastrophes periodically occur. This past has been deposited on its present form and condition.
It is impossible to write a detailed history of the Black Sea with the exact dates of all its changes. But with a sufficient degree of historical accuracy briefly this history is quite realistic.
About 200 million. years ago, the vast Tethys Ocean was located in what is now southern Europe and Central Asia. It connected the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, which already existed in those ancient, prehistoric times.
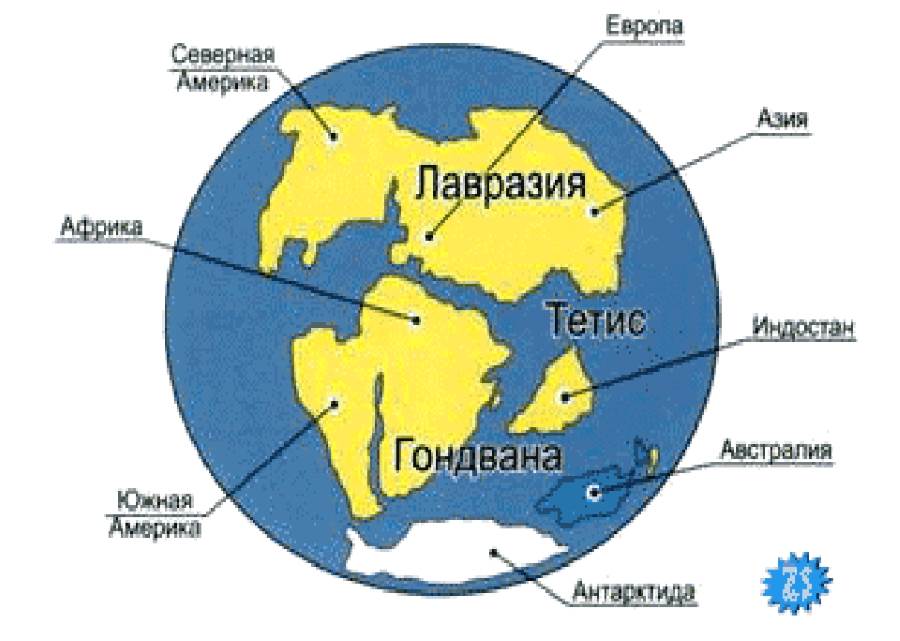
And Tethys was located between the oldest continents of our planet, Gondwana and Eurasia. The last continent connected together modern Europe, North America, and parts of Asia, which then began to diverge and collide with each other.
The Ancient Continents of Planet Earth
The split of Gondwana and the abolition of Tethys
About 60 million. years ago, the ancient continent of Gondwana began to move northward and collided with Eurasia, resulting in the destruction of the Tethys Ocean, i.e. the direct link between the Atlantic and the Pacific was eliminated.
The ocean itself is about 10 million. years ago broke up into several enclosed bodies of water, among which the ancestor of the Black Sea emerged a few million more years later. Today this sea has a connection exclusively with the Atlantic and is only partially salty.
Sarmatian Sea
About 7 million. years ago, global changes in the Earth’s crust began to take place in the area of the extinct Tethys salty ocean, resulting in the formation of new mountain systems and the joining of southern Eurasia.
This is when the Alps, Carpathians, Balkans, Caucasus and other mountains that exist today were born. Several huge enclosed water basins with low salinity appeared on the site of Thetis, so the ocean turned into several lakes.
One of these basins was later given its first name, the Sarmatian Sea. Geologists believe that this sea many millions of years ago stretched from Central Europe (Austria) to Central Asia (Tien Shan).
That ancient sea was cut off from the oceans and included today’s Azov, Aral, and Caspian Sea. Over time, thanks to the flowing rivers, it became more and more fresh. The fauna and flora of the salt ocean have been lost to fresh water for hundreds of years.
However, many animals of the dead salty Tethys Ocean continued to inhabit the Sarmatian Sea for a long time, despite the desalination of its waters. Skeletons of ancient seals, whales and sirens are still found by scientists in the depths of the Black Sea.
The Meotic Sea
No later than 3 million. years ago, the sea significantly decreased in size, reconnected with the salty Atlantic and got a new name – the Meotic Sea. As the salinity of the water increases, the animals and plants that live in such water arrive from the ocean.
The connection took place across the modern Mediterranean Sea, which also flowed into the Atlantic at that time. This ancestor of the Black Sea never again connected directly with the Pacific Ocean, and the Atlantic occasionally broke through to it.
Pontic Sea
Another million years later, the connection with the ocean was severed, and there was practically a freshwater Pontic Sea. The Azov, Aral, and Caspian Sea are already forming their borders, but they communicate with the Black Sea through the present-day territories of southern European Russia.
In a Pontic sea or lake, flora and fauna able to live only in salt water die out, and living organisms and plants adapted to brackish or almost fresh water appear. These relics still inhabit the Black Sea today.
Chaudin Lake
Subsequently, the salinity of the Pontic Sea, its boundaries and inhabitants changed several times. During this period of its history, it was named Chaudin Lake. A million years ago the lake became almost fresh and quite distant from the ocean.
Animals of the Pontic species began to inhabit here, i.e. adapted to live in partially salty water. This species still lives today in the Black Sea, the modern salinity of the water is quite satisfied with it. The low salinity is a feature of this sea.
Lake Euxine
 About half a million years ago, a rapid melting of the ice began, the body of water increased, markedly changed its borders, strongly desalinized and got a new name – Lake Euxine.
About half a million years ago, a rapid melting of the ice began, the body of water increased, markedly changed its borders, strongly desalinized and got a new name – Lake Euxine.
At this time, the outlines of the modern Black Sea already appear, but it continues its close connection with the Caspian Sea, which at this time was also significantly desalinized by glacial waters, and its fauna was dominated by animals of the Pontic species.
Karangate Sea
Scientists believe that 200,000 years after the melting of the glaciers, by the standards of the history of the geology of our planet – recently, the Dardanelles Strait arose, connecting the current Black and Mediterranean Seas, and the salt water began to flow into the Euxine Lake.
The modern Black Sea got its connection with the salty Atlantic Ocean, i.e. from a lake turned into a real salty sea. And its salinity at that time greatly increased and was noticeably higher than today’s level.
Consequently, new representatives of fauna appeared in the Black Sea, which feel perfectly well in the salty waters. They came here from the Atlantic, passed through the Mediterranean, and pushed back the Pontic fauna that lived there.
The latter began to inhabit various estuaries, estuaries of rivers, of which there are a great many on the coast of the future Black Sea. This went on until the next cataclysm: the emergence of the modern Bosphorus Strait as a result of a cataclysm with the Earth’s crust.
Black Sea
The enormous sea was able to connect across the Mediterranean to the ocean about 8,000 years ago through the present-day Bosphorus Strait. Scientists believe: the strait came into being during a powerful earthquake, it was the World Flood, described in the Bible.
At that time, the water level in the Black Sea was lower than in the Mediterranean, and the water simply gushed through the ruined isthmus on the site of the present-day Bosphorus. The ancient people who lived on the shores of both seas perceived it as the end of the world.
The version of the Flood is confirmed by the story in the Bible, or rather in the Old Testament, of how Noah moored his ark to Mount Ararat. This is quite likely if the water from the Mediterranean and the Black Sea flooded the entire Caucasus.
In those times, many ancient cities and settlements were destroyed, many tribes and entire peoples disappeared irrevocably, the coastlines of many seas were changed. All this was destroyed by earthquakes causing huge tsunamis, a real flood, etc.
Ancient names of the Black Sea
- Sarmatian Sea;
- The Meotic Sea;
- Lake Pontic;
- Chaudin Lake;
- The Ancient Vexin Sea;
- Karangate Sea;
- The New Vexin Sea;
- Black Sea.
Some names of the Black Sea of different human civilizations
In periods of several tens of millennia, remaining in the memory of mankind and preserved in the ancient epics and chronicles, the Black Sea had several names:
- The Sea of Spera (Ancient Georgia);
- Pontus of Aksinu (Ancient Greece);
- The Scythian Sea (from Strabo’s Geography);
- Pontus of Euxine (Ancient Greece);
- Russian Sea (“The Tale of Bygone Years”);
- Black Sea (translated from the Turkic “Kara Deniz”).
Features of the Black Sea
Today, the Black Sea combines signs of a freshwater lake and a salty sea. It has a small salinity of about 17%, and the ocean salinity is about 35%. Many full-flowing rivers – Danube, Dnieper, Buk, etc. – flow into our sea, desalinating it.
Currently, the water level in the Black Sea is higher than in the Atlantic Ocean, so the Bosphorus and Dardanelles have quite a strong current in the Mediterranean. In the Black Sea there are two opposite currents.
Why is the Black Sea called that?
There are several versions or legends about it:
- In ancient times, when the Hellenes explored this sea, they called it at first Pontus of Aksina (inhospitable sea) and then Pontus of Euxin (hospitable sea). They changed their opinion after the development of the Crimea, which they called Tauris.
- There is a legend that the ancient Scythians, who came from Asia to the Black Sea, saw in its waters a huge number of dark algae that spread out over many kilometers. Perhaps that is how the name of the Black Sea came about.
- There is an opinion that the Black Sea got its modern name from ancient tribes, because. During storms and tempests, its waters take on a very dark color. Black clouds hung over the sea, which terrified ancient mariners.
- The most popular version among scientists: at a depth of more than 100 meters there is no life in the waters of the Black Sea due to a large accumulation of hydrogen sulfide. While the maximum depth of the sea is more than 2,000 meters.
Probably because of the absence of living organisms in the depths of the sea, it is called the Black Sea. There are many versions of why there are huge accumulations of hydrogen sulfide in the sea, but they are all purely hypothetical.
We will never know who and why called the sea the Black Sea. Today it is one of the best southern seas of Russia, giving people in the summer a lot of joy, warm water and beautiful sandy beaches.