Troy (Ilyon) is the famous ancient fortress city, which was sung by Homer in his “Iliad” and “The Odyssey. Where was Troy located and what is it famous for? What legends are associated with it? You will learn all about it in this article.
The Prehistory of Troy
Before the emergence of Troy, there was an ancient Neolithic settlement Kumtepe, it was founded about 4.8 millennium BC. Kumtepe was mostly inhabited by fishermen, who not only caught fish, but also traded them.
After a few centuries, the settlement was abandoned. But later, about 3.7 millennium BC, it was revived by new colonists who were engaged in cattle breeding and agriculture.
History of Troy
The city or state of Troy had a favorable political and economic position throughout its history: fertile land, the presence of two rivers: the Simois and the Skamander, access to the Aegean Sea, etc.
This is why ancient Troy was the most important trading center between the West and the East for many centuries in a row and was repeatedly raided, looted and set on fire by various tribes.
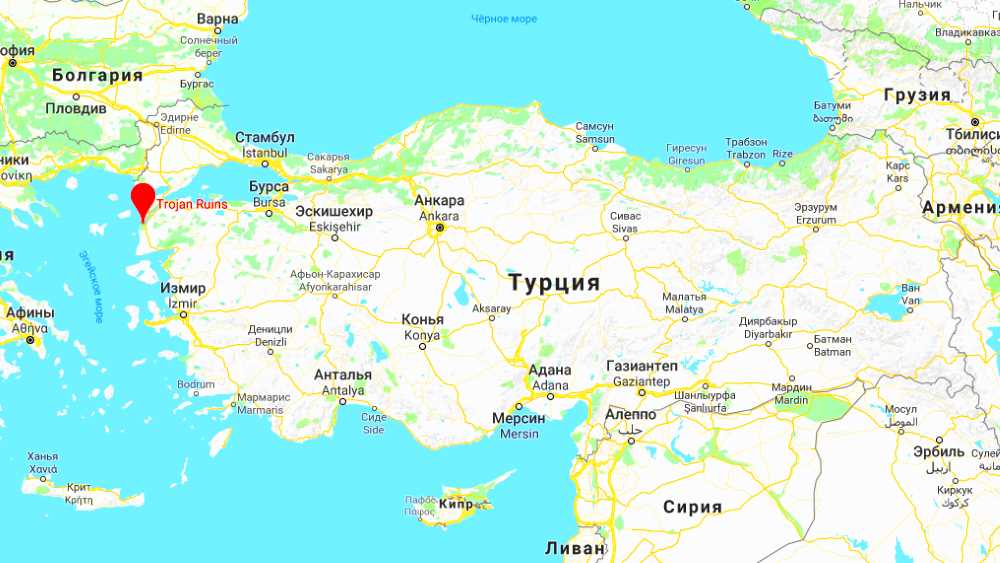
So Troy was built off the coast of the Aegean Sea in Asia Minor. Today the territory where Troy was located belongs to Turkey. The people who lived in those distant times in Troy are referred to by historians as Teukra.
The heyday of the city falls on the famous Mycenaean civilization. In addition to Homer’s epic, Troy is mentioned in the ancient cuneiform tablets of Taruish, the ancient Egyptian papyri of the time of Ramses III, Mycenaean texts, etc.
Historians have not reached a consensus on the origin of the Trojans. They are also still debating whether Troy is the name of a state or its capital. The information that has come down to us from the depths of time is clearly insufficient.
The Legend of the Foundation of Troy
According to Greek mythology, Troy was founded by a young man named Il. The Phrygian king generously rewarded him for winning the contest, gave him 100 slaves and a cow in addition, and ordered him to establish a city where the cow would want to rest.
The cow decided to lie down on Ata’s hill. It was on this hill that the legendary Troy or Ilion was founded. Zeus blessed the founding of the city, promised to protect it, and sent Ilu a wooden image of Athena.
According to legend, some ancient Greek gods were personally involved in building the walls of ancient Troy. Apollo and Poseidon served the king of Troy and built a strong wall of large blocks of stone around the city.
Excavations of Troy
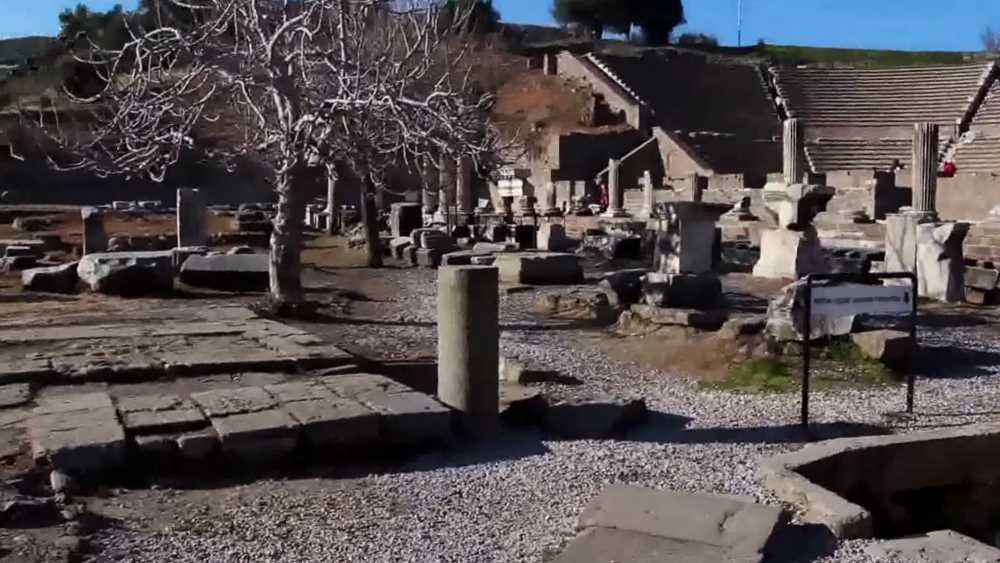

For a long time, European scholars have argued about where Troy was. In the early 19th century, English historian McLaren suggested that the ancient city was located under the hill Hissarlik.
Already at the end of the 19th century German archaeologist Schliemann began active excavations in this place. He was the man who discovered the ancient city of Troy to his contemporaries.
Today, Schliemann’s archaeological finds are preserved in the Pushkin Museum, the Hermitage, and other museums around the world. Excavations continue on the Gissarlik Hill, and the ruins of nine ancient fortresses from different eras have already been exposed.
Layers of the ancient city of Troy
Archaeological excavations have revealed several ancient cities, each of which has been named Troy. Archaeologists count a total of nine layers of ancient Troy, not counting the Neolithic settlement.
Troy I (3rd millennium BC)
It was a small fortress-like settlement with simple earthen walls and houses. Most likely, it died as a result of the fire. Pottery similar to that found in Bulgaria has been discovered.
Troy II (2.5 millennium BC)
This rich settlement was discovered by Schliemann himself. Among other things, a German archaeologist found the famous Priam treasure with many weapons, precious jewelry, gold tableware, etc.
Troy III-IV-V-VI (2.3-1.3 millennium BC).
These layers tell of the decline of Troy, the earthquake that befell it, and later the gradual reconstruction and growth of the ancient city, turning it into the capital of a strong state.
Troy VII (1.3 to 0.9 millennium BC).
It was during these times that the famous Trojan War took place, which made this ancient city famous for centuries. Homer recounted this war in his Iliad and Odyssey. Eventually the fallen Troy was taken by the Phrygians.
Troy VIII-IX (900 – 350 BC)
At this time, the history of Troy and ancient Greece are closely linked. The city is inhabited by Greeks, it is visited by the famous Greek king Xerxes, Troy it becomes quite a major center of Hellenic culture.
Troy X (300 B.C. to 500 A.D.)
Later Troy was taken over by the Persians, and then the city came under the rule of Alexander the Great. During the Roman Empire, Troy slowly began to revive, was exempted from taxes and greatly expanded.
However, in the 5th century AD. Troy was conquered and finally destroyed by the Turks who came to Asia Minor. In the 6th century, the last settlements of people who lived on the site of the once legendary Troy disappeared forever.
The Language and Writing of Troy
Some scholars believe that the Trojans spoke a language close to Phrygian, while others believe that they were of Luvian origin and spoke Luvian. All assumptions are based on ancient Greek legends.
Archaeologists discovered during the excavations of Troy several clay pots with unknown signs, which were thought to be Trojan writing. However, not all scientists agree with this.
Trojan War

The city of Troy or the state of Troy is primarily known to mankind by the Trojan War, described in detail by Homer in the epics The Iliad and The Odyssey, as well as in many pre-Homerian epics.
Scholars study these epics both as historical treatises and as works of fiction. They have long noted that many of the events described in them existed in historical reality.
Homer and the later authors of The Iliad and The Odyssey, in describing the events of the Trojan War, introduced real and fictional heroes into their works. And the war happened, according to historians, at the turn of the 13th-12th centuries BC.
An occasion for war
According to the epic, the occasion for the declaration of war was the kidnapping of Helen by King Paris of Troy. As a result of this incident, the kings of ancient Sparta and Mycenae began to persuade other Greek kings to go to war on Troy.
According to legend, under the leadership of the Mycenaean king Agamemnon, 100,000 warriors gathered for war, who in more than 1,000 ships reached Asia Minor and stationed themselves in the Trojan valley.
Beginning of the war
Prince Paris did not agree to give up Helen and make peace. And Agamemnon’s troops could not take such a fortified city at once. So they stopped near Troy and ravaged the surrounding settlements for sustenance.
This went on for nine years, exactly as long as the Trojan War was predicted to last. Agamemnon’s troops began to quarrel among themselves out of idleness. Finally, a time was set for the battle between the Trojans and the Greek king’s army.
The Battle of Trojan
The battle began with a duel between Paris and Menelaus over the honor of the kidnapped Helen and her treasure. In the end, Paris was defeated and Menelaus nearly killed him, after which the first battle of the Trojan War finally began.
The Trojans began to win the battle, and Agamemnon decided to flee the battlefield. However, his armies once again overpowered the armies of Paris and approached the walls of Troy. The Trojans did not surrender and stormed the Greek military camp. None of the participants in the battle conceded.
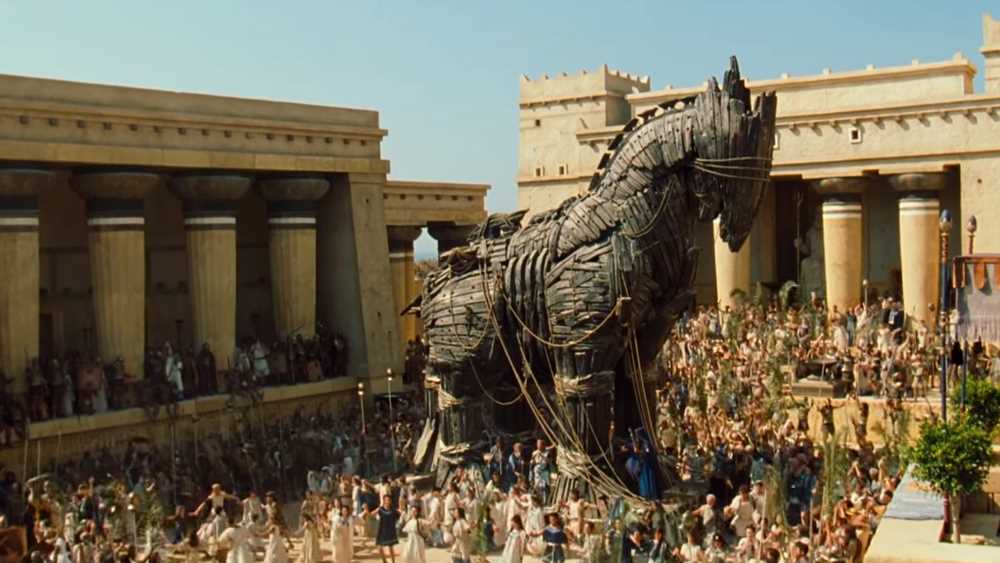
Trojan Horse
An army of Ethiopians led by King Memnon came to the aid of Paris, but in the end the Ethiopian king was killed by the enemy’s weapons. Achilles and Odysseus realized that Troy could not be taken by force and courage, but only by cunning.
For this purpose, Eleus built a huge wooden Trojan horse, inside which Odysseus and Agamemnon’s bravest warriors hid. The rest of his army pretended to have left the battlefield and left on ships.
The Trojans left the city and inspected the Trojan horse. On the advice of the traitor, they led him into Troy to the acropolis and dedicated him to Athena. At night Odysseus and his warriors emerged from the horse, they opened the gates and, together with the returning army, took possession of the city.
Historical Interpretation of the Iliad and the Odyssey
In ancient times, the Trojan War was considered a real historical event. Some modern scholars do not take this fact as an absolute truth, but many historians agree that there was a war after all.
Many experts see various allegories in this literary work. For example, the wanderings of the Jews under the leadership of Moses, their struggle for the Promised Land, the fall of Jerusalem, the retelling of the acts of the apostles, etc.
Modern Troy

Today, Troy is a museum city located in the highlands of Asia Minor in Turkey. Millions of tourists visit the museum every year, and archaeologists and other scientists continue to work at the site of the excavations.
Tourists can visit the ruins of the ancient city from May to September, they look just fantastic. In order to get acquainted with all the exhibits, you can invite a Russian-speaking guide.
But most of all tourists are interested in a copy of a wooden Trojan horse made by Turkish craftsmen. You can climb inside it and feel like a real Odysseus.
Remember, there are many travelers from all over the world interested in Ancient Troy. Therefore, you should calculate the time correctly so that you can at least get close to the city-museum.
Separately, you can visit the Museum of Excavation and examine there ancient and modern photos, models, exhibits that tell about the discovery of Troy and its treasures. You can also go to the Temple of Athena, visit a modern concert hall Odeon, etc.
Attractions near Troy
- Alexandria of Troas. This city south of Troy was founded by the ancient Greeks in the 4th century BC. Later it passed to the Roman Empire and was named after Alexander the Great. It is interesting that Alexandria of Troas is mentioned in the New Testament.
- Ass or Behramkale. This city is famous for the fact that in the time of Plato and Aristotle there was a philosophical school attended by famous philosophers of antiquity. You can also see the Murad Mosque, ancient tombs and caravanserais.
How to get to Troy?
A bus leaves every hour from Chenakkage, 30 km from Troy, which will take you to the excavation site in half an hour. You can also get here directly from Istanbul, Bursa, or Izmir by shuttle buses.
Where is Troy on the map?
Troy on a map of Turkey
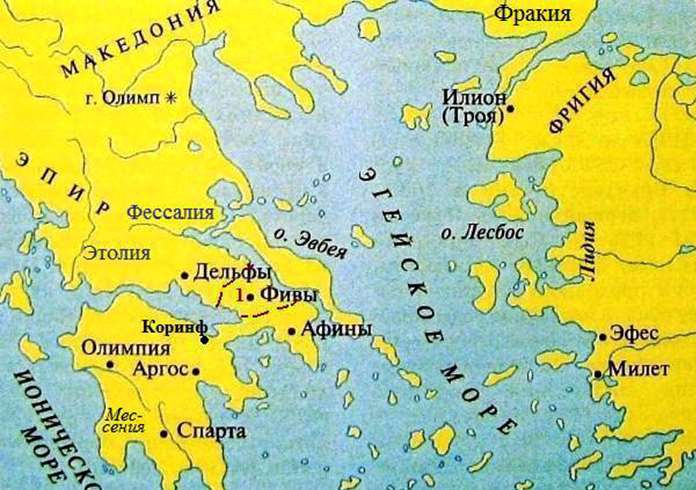
Troy on the map of the ancient world
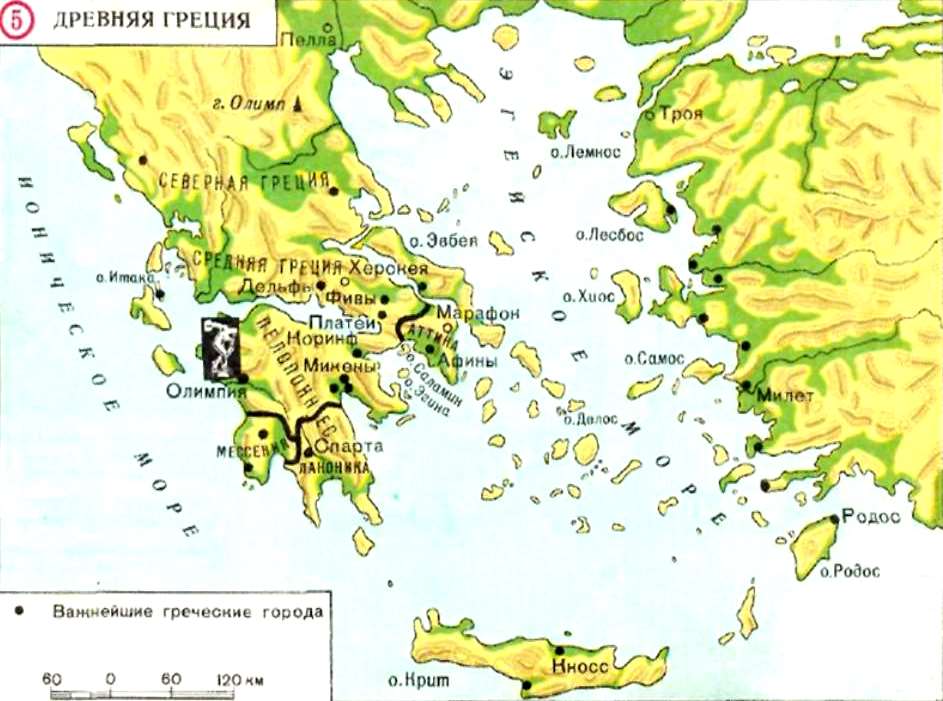
Troy on the map of ancient Greece